Learning Stories
by
Mario deSantis
mariodesantis@hotmail.com
“I am a Canadian, free to speak without fear, free to worship in my own way, free to stand for what I think right, free to oppose what I believe wrong, and free to choose those who shall govern my country.” - -The Rt. Hon. John Diefenbaker, Canadian Bill of Rights, 1960
“The whole judicial system is at issue, it's worth more than one person.”--Serge Kujawa, Saskatchewan Crown Prosecutor, 1991
“The system is not more worth than one person's rights.”--Mario deSantis, 2002
Ensign Stories © Mario deSantis and Ensign
|
System Dynamics in Education: Commonality of Structure and Behaviour By Mario deSantis, March 29, 1999 |
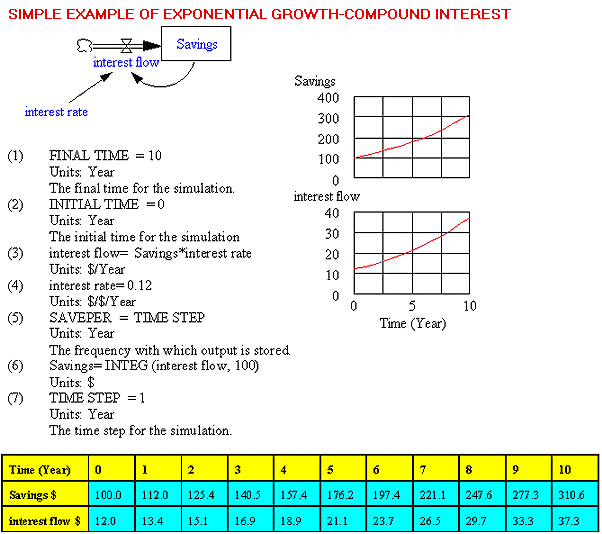
| In our past articles on System Dynamics we have emphasised the need of educational reform under the understanding that knowledge is constructed and that learning is a natural extension of living and relating to one another. We also mentioned that schools must become Learning Organizations and use the related comprehensive discipline of System Thinking(1) for increasing the learning capacities of our students. As a consequence, the role of the teacher would not be one of transferring his knowledge to the students but one of providing the proper different environments for facilitating the natural learning of all the students. Students must become engaged(2) in their studies and use the new technologies, including the Internet, along with the educational approach of System Dynamics for building models of the real world and simulate their behaviour over time. System Dynamics(3) (4), as a generic methodology to build complex models, provides a common denominator for learning many academic disciplines, such as mathematics, biology, chemistry, ecology, physics, history, and literature. Models can be constructed from the microworlds of these disciplines and the understanding of their structures and behaviour transcends any particular discipline. It is important to point out that one of the major failures of our school system, and indirectly of our social decision-making processes, is the neglect of the time element associated to the learning of our academic disciplines. In schools, knowledge has always been presented as a series of static facts disassociated from time. And, it is not an understatement to say, that this static view of the world has produced the many current incompetent leaders, who are paid the big buck to make the so called tough decisions: black or white, shoot or not shoot(5), pro-life or pro-abortion, and so forth. I have provided in this article the documentation of the model "SIMPLE EXAMPLE OF EXPONENTIAL GROWTH-COMPOUND INTEREST" developed through the effective Vensim PLE(6) software. The purpose for presenting this model is to describe the basic terminology used in System Dynamics and at the same time appreciate the kind of fundamental basic learning it provides. The model represents the accrual over a 10 year period of an initial $100.00 saved in a bank account at the fixed interest rate of 12% compounded annually. The model is made up of variables, which are the components of the system, and of arrows describing the interrelationships between the variables. Variables which are stocks(7) are defined by a box, and variables representing flows are defined by a directional valve. In our case, the variable "Savings" is a stock and it is expressed in $, while the variable "interest flow" is a flow and it is expressed in $/year; that is the variable "Savings" is the sum of the initial deposited of $100.00 and of the related interest flows over the next 10 years. All the variables have numerical formulations through equations; in this case the "interest rate" is set at .12 and the variable "interest flow" is found by multiplying the variable "Savings" by the "interest rate" at the end of every year for the 10 year period. The concepts of stock and flow are omnipresent in our daily lives and provide an earlier understanding of the mathematical concepts of integral and derivative(8). The building of models is an iterative and creative process. Further, the setting of relationships and equations for the variables is a critical thinking process which includes particular attention to the units of measure of all the variables in the model. The exponential behaviour of the accumulation of the variable "Savings" is a very common phenomenon in our biological and social environments and therefore the same model, structure and behaviour can be found in the study of other parts of the real world. This is the beauty of System Dynamics, the opportunity to have a comprehensive, multi disciplinary, participative and unambiguous approach to address our realities and learn how to learn together.
|
| Endnotes 1. Systems Dynamics in Education: Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics, by Mario deSantis, February 26, 1999. Published in the North Central Internet News 2. We have today, the technologies to produce "virtual realities", where people can feel, see, and experience "real realities". We can specifically refer to the current flight simulators to train pilots of commercial or military plane jets. We can also refer to the virtual realities available on CD-ROM such as SIMCITY 3000, by Electronic Art, EMERGENCY ROOM 2, by Legacy Software, and TITANIC: CHALLENGE OF DISCOVERY, by Robert Ballard, who envisions virtual explorations conducted on the Internet. Says Ballard "...We could replicate your head... You can hear, you can see,... and you can talk..." (Playing Games on the Internet, by Suzanne Kantra Kirschner, Popular Science Magazine, December 1998). However, Barry Richmond clarifies that "...no matter how advanced the technology gets, it will always be only part of the solution. If people are to make sense of their experiences in virtual realities, they must have the capacity for understanding the underlying closed-loop framework that is generating these experiences. They must be capable of thinking both systemically and dynamically. In short, they must be systems thinkers..." (Systems thinking: critical thinking skills for the 1990s and beyond, Barry Richmond, Road Maps 6, System Dynamics in Education Project, MIT http://sysdyn.mit.edu) 3. A general definition of System Dynamics would be the discipline for learning the real world through feedback computer modelling and simulation, and it would certainly include the mentioned virtual realities. 4. System Dynamics in Education Project, System Dynamics Group, Sloan School of Management, Massachusetts Institute of Technology http://sysdyn.mit.edu 5. Regina Police Shoot and Kill 15 Year-Old, by Timothy Shire, September 12, 1998. Article published in the North Central Internet News 6. Vensim PLE is the free of charge introductory educational package published by Ventana Systems, Inc. http://www.vensim.com 7. Stocks are also called accumulators or levels. 8. At any time the derivative of the stock is equal to the related flow.
|